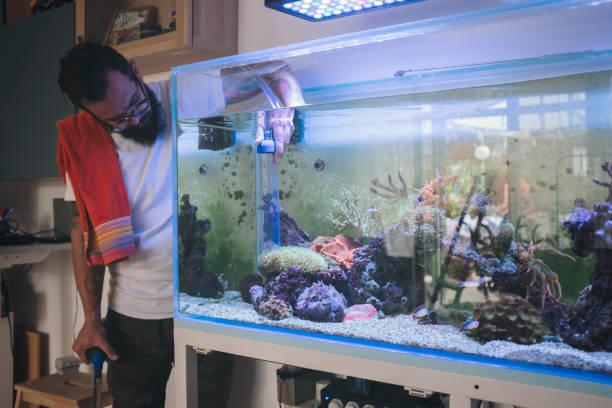
You’re getting an aquarium for your home or business and one of the first decisions to make is whether to go for freshwater or saltwater. Both are beautiful and complex in their own way, with amazing diversity and endless possibilities. But before you become a full-time hobbyist get to know the differences between saltwater and freshwater fish tanks.
Saltwater Vs Freshwater Fish Tank
Choosing between a saltwater or freshwater ecosystem is the key decision. Both options can bring equal satisfaction. Each comes with its own set of rewards and challenges. Your aquarium may become a lifelong passion if you pick the right one and stick to a regular upkeep schedule. Here’s what you should consider when comparing saltwater fish vs freshwater fish aquariums.
1. Filtration System
Live rock by itself has enough power to provide biological filtration for reef aquariums. And there’s no need for biomedia at all! Reef systems might need GFO sometimes, but generally, you can skip chemical filtration. Freshwater aquariums don’t need chemical filtration, and most reef aquariums don’t either.
A reef aquarium’s mechanical filtration can be done easily. In fact, it’s better not to have mechanical media in the system because they work better without it. Also, since there are fewer fish compared to freshwater systems, there’ll be much less waste.
2. Fish Diversity
Ever wondered which is better freshwater or saltwater fish? Well, freshwater fish are found in several colors, sizes, and shapes. Fish like guppies, tetras, and bettas are common choices for freshwater tanks. Beginner fish tank enthusiast? These fish are good picks because you can take their care much more easily.
Saltwater aquarium fish are known to have bright colors and odd shapes. They also tend to move around and interact more than freshwater fish, which is why people think saltwater aquariums are hard to preserve. Clownfish, tangs, and angelfish are some popular choices.
3. Water chemistry
Unlike freshwater tanks, using tap water is suitable for saltwater setups. In nature, the water surrounding a reef contains almost no nutrients. It means marine algae can grow in low-nutrient conditions. Even the small amounts found in tap water can turn a saltwater aquarium into an algae-filled tank. So, get water that’s been through reverse osmosis (RO) and deionization (DI). RO/DI water goes through extreme filtering to get rid of debris.
Pure water doesn’t carry electricity, and that’s how people measure RO/DI’s purity: by checking how well it conducts electricity. Keep in mind that RO systems for drinking water don’t cut it. Use a proper RO/DI system to get water clean enough for a saltwater aquarium.
4. Equipment
A tank with a hood bottom substrate and a filter to process the water five to ten times are essential for both aquariums. Your level of interest can determine the size of freshwater tank. Options range from a one-gallon tank for a single betta fish to a 350-gallon show tank. You’ll need a cover over the tank to stop quick water loss. Add a light to house plants or see the fish at night. Freshwater tanks also need an air pump to add oxygen and a heater/thermometer to monitor the temperature.
Saltwater tanks need to be at least 30 gallons to get good results. Small changes in water quality have a bigger impact on smaller tanks making them tough to use for a marine system. Besides the parts needed for freshwater aquariums, try using a protein skimmer in saltwater tanks to get rid of organic waste. A hydrometer is also important as it will help measure the amount of sea salt which should be around 3% of the water.
5. Feeding
Freshwater fish eat prepared food. They mostly eat what you feed them. But saltwater fish species are wild. And what’s more surprising? They haven’t eaten since they were caught in the wild so feeding them can be a bit tricky. Processed or canned food doesn’t work well for saltwater fish. When feeding them we recommend top-quality frozen food for the first few weeks and then slowly transition to nutrient-rich marine pellets. Frozen feed helps in their survival but again this is only for short-term use. For regular feeding, top-quality pellets are the best choice. You can also choose live food for aquarium fish and create a more enriching aquatic environment.
6. Decor and Plants
Instead of adding plants to saltwater tank, adding corals and live rocks will add a whole new level of coolness. Installing a reef system needs specific lighting requirements and a bit more work for a living ecosystem maintenance. Using crushed coral or sand as a substrate will encourage the growth of microorganisms and bacteria that will help the tank thrive.
Sand or gravel, which is best? It depends on the fish type, gravel, or sand. Gravel is easier to clean but sand provides a place for certain species to rest. There are tons of decorations for freshwater tank including fake corals, rocks, and sunken ships won’t deteriorate when dipped in water. What about adding a mix of rocks, plants, woods, and sand? Just create an environment that suits your taste!
7. Costs
The main difference between freshwater and saltwater aquariums is often the price. You might have heard freshwater tanks cost much less than saltwater ones, but is this true? Saltwater aquariums need extra gear to run properly. The price of this extra equipment and marine animals is often twice as much as for freshwater tanks. Most freshwater fish cost between 1-10 dollars. But for saltwater fish, the price depends a lot on the type of fish and how easy it is to find. So, they can cost anywhere from 20 dollars to hundreds of dollars.
Saltwater Vs Freshwater Aquarium Maintenance
Salt water or fresh water aquarium needs constant checks to keep fish healthy. Yet, the way you clean fish tank may differ.
For freshwater tanks, change the water, and rinse the filter often. It helps get rid of waste and keeps the water sterilized. Saltwater tanks need even more work. It is important to change the water more often, clear the protein skimmer, and check the water’s chemistry. They also need nitrate, phosphate free water, and control of nuisance algae. Keeping salinity, pH, and calcium stable can be tricky. Regular testing and adjustments are key to a healthy saltwater environment.
When you’re trying to decide between the two, you need to think how they’re different. Freshwater fish are usually easier to take care of and don’t cost as much. But saltwater fish come in more colors and shapes. They also tend to be more fun to watch and interact with. No matter what kind of fish you pick, setting up the tank right and giving fish good food is essential to keep them healthy and happy. At EasternMarine Aquarium, we supply premium fish feed. Our feed is species-specific. We believe every feed can make a change and a future for quality, adaptability, and well-being.
In A Nutshell
Saltwater aquariums aren’t harder to start than freshwater aquariums. But let’s face it, there’s more to learn in the saltwater hobby. Also, maintenance wise it’s more demanding in the saltwater side. So note these differences before you decide on your first or next aquarium. Most importantly the livestock, equipment, and cost are what will ultimately decide.
Hope this guide has helped answer the question, “Which is better saltwater or freshwater aquarium?” When you are ready, shop for aquarium equipment, supplies, livestock, and much more only at EasternMarine Aquarium.